One of the most common product specifications that people often neglect is the amperage, which is measured in amp units or amperes, that is, unless you are talking about batteries or power banks that display ampere-hours on the device. With regard to the question stated, how many amperes does the device actually use during operation? This may be a concept that you may usually not think about. But knowing this will be a great help for you as you assess how electrical flow in a circuit actually behaves.
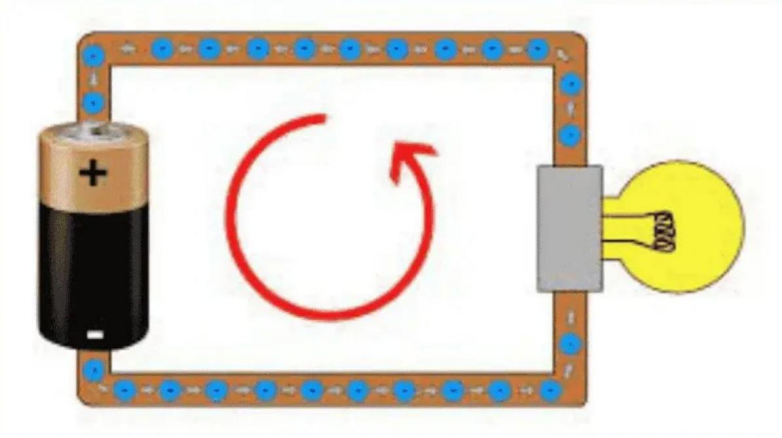
How to Determine the Amperage of Your Device?
Check the labels
The surefire way to know the amp units or the amperage of your device is to look at the label. The specific details of your device are located in the product description on the online store where you bought the device. It is also indicated in the operations manual of the device included in the package. If you do not have access to either of the two, you can always do a quick search for your product and find the manual accompanying the device. You will know the rated amperage that your devices operate in. You have to keep in mind that the rated amperage on the labels is the maximum current that the device is designed to safely handle.
Compute it
If you cannot find the manual anywhere online, you may still get it through a particular formula. You can divide the power measured in watts by the voltage that is measured in volts. The voltage and power are both usually printed on the body of the device. As you can see, the amperage is directly proportional to the power and inversely proportional to the voltage. This means that, in effect, a surge in amperes may mean a voltage drop in the circuitry, which can cause fuse malfunctioning of circuit breaker tripping.
Use a power meter
Another way to compute the actual amperage that your device actually utilizes is through a power meter. This is a simple yet powerful tool that you can use to measure the amperage of your device. To do this, you just need to plug the power meter into the electrical outlet and then plug the device into this tool. The power meter automatically displays all the details of the device, including the number of amperes, power in watts, and voltage. If you are using USB devices, you now have USB meters that you can use as well.
Real-world examples
This should serve as a guide for you in monitoring the actual amperage of your devices. Small devices should use around 0.5 to 2.4 amperes. Bigger laptops and other mobile devices are able to have around 3 amperes. Televisions also have the same rating as computers and laptops. In determining the actual amperage of the device, you must ensure that the voltage supply for the device is sustained. You also have to take note that amperage does not increase over time with devices. They also get the rating that they actually need to operate. However, current surges may still occur.

Conclusion
Knowing the amp units or amperage of your devices will help you keep them safe, along with the electrical lines where the device is connected. As mentioned above, a surge current may happen, which may cause damage to the device. If you incorporate safety measures into the device, you are protecting the device as well as other equipment connected to the same electrical line. It is a good thing that electrical lines in the home also have protection, such as proper grounding and tripping of circuit breakers, to prevent these incidents. In these cases where problems persist, troubleshooting will be easier because you know the amperage of your device.